In this article:
Setting Up Scheduled File Deletion in MinIO
Scheduled Clearing of the MinIO File Storage
When the MinIO local file storage is used, set up scheduled file deletion to free up memory. For example, during advanced logging of events with the Debug status, MinIO saves JSON files with the responses obtained during executing requests to data sources and stores them in the debug-logs-storage section at: debug_logs/<environment name>/<project name>/<resource name>.
Used sections in MinIO in the Buckets directory:
backups. It is used to store backups of PostgreSQL databases when using cluster configuration of Foresight Mobile Platform.
debug-logs-storage. It is used to store JSON files with responses from data sources, database, or mobile platform server when advanced logging of data source requests is executed.
django-local-storage. It is used to store files loaded to local storage of each project.
media. It is used to store application distributions and data source server certificates.
Scheduled file deletion from the MinIO storage is set up in the MinIO we interface or via the command line.
Setting Up Scheduled File Deletion in MinIO
To set up scheduled file deletion, open the MinIO application at:
http://<IP address or DNS name of server>:9001
After executing the operation the MinIO application opens. Go to the Administrator > Buckets section on the side panel:
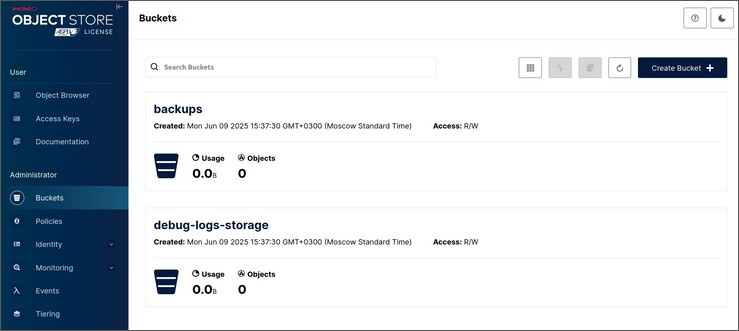
The Buckets directory contains MinIO sections: backups, debug-logs-storage, django-local-storage, media.
Creating Schedule
To create a schedule, according to which files will be deleted from the storage:
Open the MinIO section. Consider the example of schedule creation in the debug-logs-storage section:
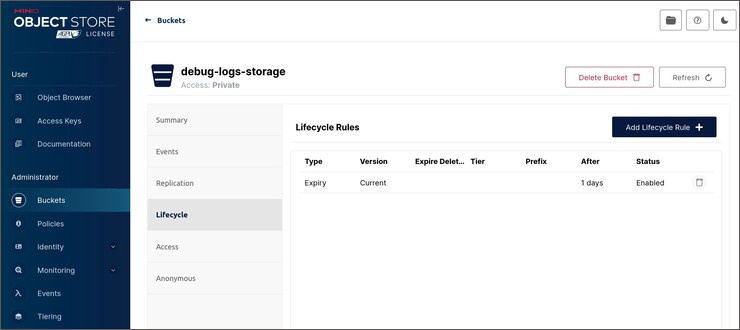
Create a rule that determines file storage time using the Add Lifecycle Rule button in the Lifecycle subsection. Clicking the button opens the Add Lifecycle Rule dialog box:
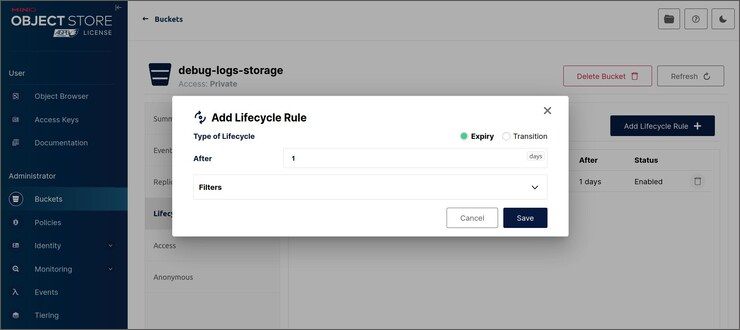
Set file storage time in days in the After parameter.
Click the Save button.
Repeat steps to create several rules in different MinIO sections.
After executing the operations a schedule for deleting files from the storage is created based on the created rules.
Deleting Rule
To delete a rule that determines file storage time from schedule:
Open the MinIO section. Consider the example of schedule deletion in the debug-logs-storage section:

Click the
 Delete button next to the existing rule.
Delete button next to the existing rule.
After executing the operations the rule is deleted from schedule.
Setting Up Scheduled File Deletion via Command Line
Schedule creation and file deletion via command line is given for standalone configuration of Foresight Mobile Platform.
Creating Schedule
To create a schedule, according to which files will be deleted from the storage:
Make sure that mobile platform containers are running and work correctly, and check name of the MinIO container - fmp_minio_1:
% docker ps
NOTE. MinIO container name may differ when working in different versions of Foresight Mobile Platform.
Create rules that determine file storage time:
% docker exec -ti <MinIO container name> mc ilm rule add --expire-days <number of days> <path to the MinIO section>
In substitutions:
<MinIO container name>. Specify name of the MinIO container.
<number of days>. Set file storage time in days. After this time the files are deleted.
<path to the MinIO section>. Specify path to the MinIO section in the Buckets directory: backups, debug-logs-storage, django-local-storage, media.
The example of command:
% docker exec -ti fmp_minio_1 mc ilm rule add --expire-days 1 local/debug-logs-storage
After executing the command the rule is created, according to which files will be deleted from the debug-logs-storage section the day after they are loaded to the storage.
If the rule is successfully created, the message is displayed:
Lifecycle configuration rule added with ID `<identifier of created rule>` to <path to the MinIO section>.
For example:
Lifecycle configuration rule added with ID `d13uj9nu7g4s6pmtdk30` to local/debug-logs-storage.
If required, create several rules for different sections in MinIO.
Get the list of existing rules and make sure that new rules are created:
% docker exec -ti <MinIO container name> mc ilm rule ls <path to the MinIO section>
The example of command:
% docker exec -ti fmp_minio_1 mc ilm rule ls local/debug-logs-storage
After executing the command the table with existing rules for the specified MinIO section is displayed:
┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Expiration for latest version (Expiration) │
├──────────────────────┬─────────┬────────┬──────┬────────────────┬─────────────────────┤
│ ID │ STATUS │ PREFIX │ TAGS │ DAYS TO EXPIRE │ EXPIRE DELETEMARKER │
├──────────────────────┼─────────┼────────┼──────┼────────────────┼─────────────────────┤
│ d13uj9nu7g4s6pmtdk30 │ Enabled │ - │ - │ 1 │ false │
└──────────────────────┴─────────┴────────┴──────┴────────────────┴─────────────────────┘
After executing the operations a schedule for deleting files from the storage is created based on the created rules.
Deleting Rule
To delete a rule that determines file storage time from schedule:
Make sure that mobile platform containers are running and work correctly, and check name of the MinIO container - fmp_minio_1:
% docker ps
NOTE. MinIO container name may differ when working in different versions of Foresight Mobile Platform.
Determine identifier of the rule that should be deleted:
Get the list of existing rules:
% docker exec -ti <MinIO container name> mc ilm rule ls <path to the MinIO section>
In the substitutions:
<MinIO container name>. Specify name of the MinIO container.
<path to the MinIO section>. Specify path to the MinIO section in the Buckets directory: backups, debug-logs-storage, django-local-storage, media.
The example of command:
% docker exec -ti fmp_minio_1 mc ilm rule ls local/debug-logs-storage
After executing the command the table with existing rules for the specified MinIO section is displayed:
┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Expiration for latest version (Expiration) │
├──────────────────────┬─────────┬────────┬──────┬────────────────┬─────────────────────┤
│ ID │ STATUS │ PREFIX │ TAGS │ DAYS TO EXPIRE │ EXPIRE DELETEMARKER │
├──────────────────────┼─────────┼────────┼──────┼────────────────┼─────────────────────┤
│ d13uj9nu7g4s6pmtdk30 │ Enabled │ - │ - │ 1 │ false │
└──────────────────────┴─────────┴────────┴──────┴────────────────┴─────────────────────┘
Copy rule identifier displayed in the ID column of the obtained table.
Delete the rule by identifier:
% docker exec -ti <MinIO container name> mc ilm rule rm --id "<rule identifier>" <path to the MinIO section>
The example of command:
% docker exec -ti fmp_minio_1 mc ilm rule rm --id "d13uj9nu7g4s6pmtdk30" local/debug-logs-storage
If the rule is successfully deleted, the message is displayed:
Rule ID `<rule identifier>` from target <path to the MinIO section> removed.
For example:
Rule ID `d13uj9nu7g4s6pmtdk30` from target local/debug-logs-storage removed.
If required, delete several rules for different sections in MinIO.
Get the list of existing rules and similarly to Step 2a make sure that the rule is deleted:
% docker exec -ti <MinIO container name> mc ilm rule ls <path to the MinIO section>
When the rule is deleted, the obtained table should not contain record with identifier of the deleted rule. If all existing rules are deleted, the following message is displayed instead of the table after executing the command:
mc: <ERROR> Unable to get lifecycle. The lifecycle configuration does not exist.
After executing the operations the rule is deleted from schedule.