 To display the tab
To display the tabThe Specification tab contains the identified equation with estimated coefficients and the coefficient table.
For example:
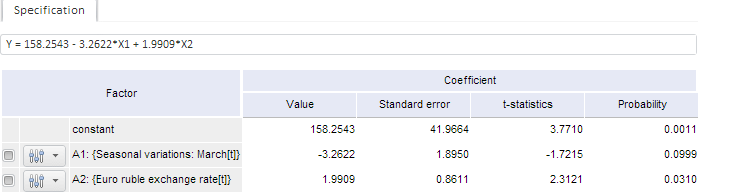
The coefficient table contains:
Factor. Name of the factor, at which the coefficient was estimated.
If executing additional operations is allowed for this factor, the ![]() button appears for the factor. To execute operations, click the button and use commands in the menu that opens.
button appears for the factor. To execute operations, click the button and use commands in the menu that opens.
Value. Estimated coefficient value.
Standard Error. An approximate value of deviation (caused by randomness of sample) of the coefficient estimation from the actual value. The greater is the value of the standard error, the less reliable is coefficient estimation.
t-statistics. It is calculated as a ratio of coefficient estimation to its standard error. It is used to check the null hypothesis that the coefficient is equal to zero, that is, it is not significant in the considered regression model. The hypothesis is checked assuming that residuals have normal distribution. It is easier to interpret the value of the t-statistics using the probability value given next to it.
Probability. The probability value for t-statistics. The null hypothesis of estimated coefficient that is equal to zero is rejected at the selected significance level (usually, 0.1, 0.05, or 0.01), if the probability is less than the significance level.
Features of working with the Specification tab depend on the equation calculation method:
NOTE. Features of working with the Specification tab for the criterion function are described in the Setting Up Criterion Function Expression section.
See also: