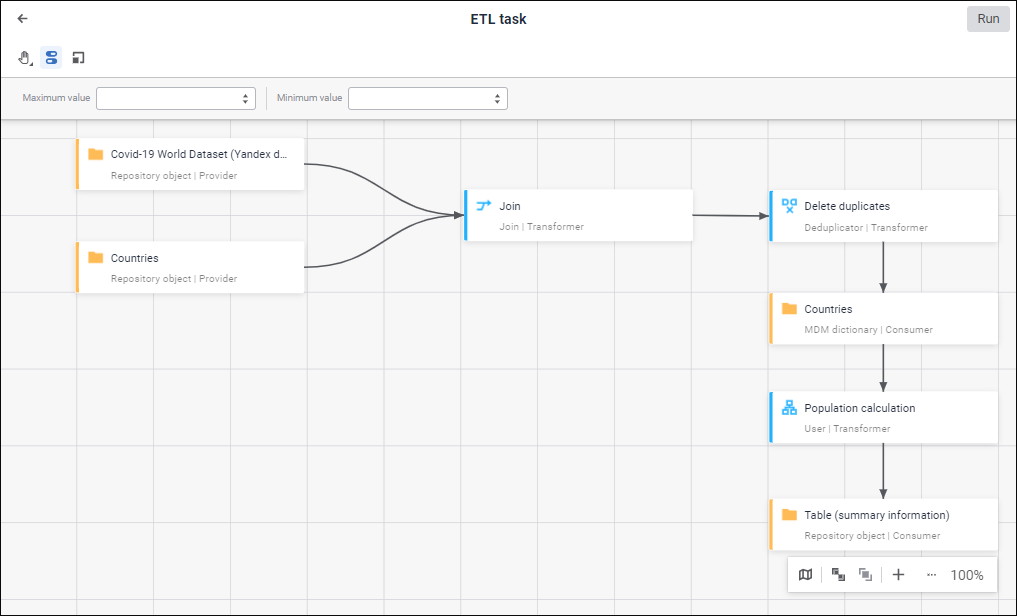
To import or export data with the ability to set up links between providers and consumers, and also set up intermediate data transformations, use the ETL Task tool:

ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is one of the key processes in data warehouse management. ETL is used for:
Extracting data from external providers (Extract).
Transformation and clearing data to get required quality (Transform).
Loading data to a data warehouse (Load).
Key capabilities:
Creating a visual data transformation schema on a single working area.
Logging execution of an ETL task.
Setting up ETL task execution order.
Extracting data from two-dimensional, relational, and multidimensional data providers.
Extracting data from and loading to external providers: OLE DB; Microsoft Access, Visual FoxPro, DBase databases; Microsoft Excel, XML, HTML, TXT, CSV, JSON files.
Extracting or loading data from repository objects: tables, attached tables, views, queries, ODBC data providers, and logs.
Extracting data from REST sources, they are accessed via the Internet.
Data transformation: merging, splitting, deduplicator, grouping, filtering, and sorting.
General description of ETL task work:

Data from providers is loaded to ETL task input. The number of providers is not limited.
Data from data provider outputs is loaded to data transformers inputs.
After the transformation data from data transformer outputs is loaded to data consumer inputs.
Data from data consumer outputs is loaded to external or internal formats.
To work with the ETL Task tool, the PP_ETL feature will be required.
To get started with the tool in the web application, see the Getting Started with the ETL Task Tool in the Web Application article.
To get started with the tool in the desktop application, see the Getting Started with the ETL Task Tool in the Desktop Application article.
See also:
Getting Started with the ETL Task Tool in the Web Application | Getting Started with the ETL Task Tool in the Desktop Application