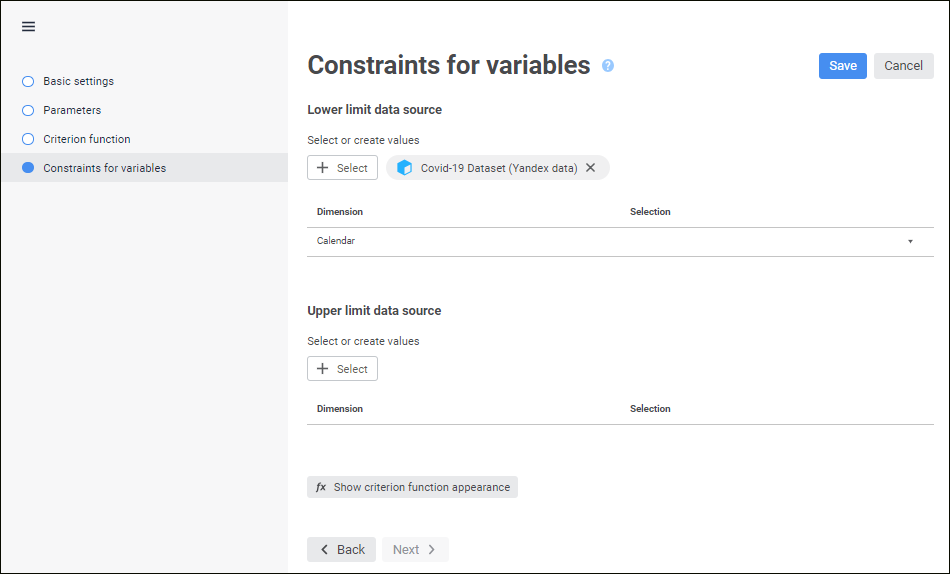
Constraints for variables enable the user to set simple conditions imposed on values of controlling variables. A condition is considered simple if it meet the following criteria:
It contains one controlling variable.
The 1 coefficient is set for the controlling variable.
For example, x1 ≥ 25 or 100 ≤ x2 ≤ 254, where x1 and x2 are controlling variables with the coefficient 1.
To set up simple constraints of controlling variables, use the Constraints for Variables page in the linear optimization block editing wizard:

Specify also the upper and lower constraint limits. Lower limit is a minimum allowed value of controlling variable, upper limit is a maximum allowed value of controlling variable. The following can be set for each controlling variable: only lower limit, only upper limit, both limits or no constraints.
For example, the constraint x1 ≥ 25 is set using the upper limit. The constraint 100 ≤ x2 ≤ 254 requires to set the upper and the lower limits.
Too enter simple constraints of controlling variables:
Select a data source to store values of upper and lower limits. This data source should contain all dimensions of controlling variables selected during criterion function setup.
To quickly select an object, enter object's name/identifier/key in the search box depending on display settings. Search is executed automatically while the searched text is entered into the search string. The list will display the objects, which names/identifiers/keys contain the entered text.
To set up displaying of repository objects in the list, click the  Display Object button and select display option in the drop-down menu:
Display Object button and select display option in the drop-down menu:
Name. Objects are displayed with their names. Default option.
Identifier. Objects are displayed with their identifiers.
Key. Objects are displayed with their keys.
Several options can be selected. Identifier and key will be specified in brackets.
Set selection by fixed dimensions of data source. All data source dimensions, except for those used as dimensions in controlling variables, are included in fixed dimensions.
As a result, constraints of controlling variables are set.
To view the criterion function, click the  Show Function External View button.
Show Function External View button.
See also: