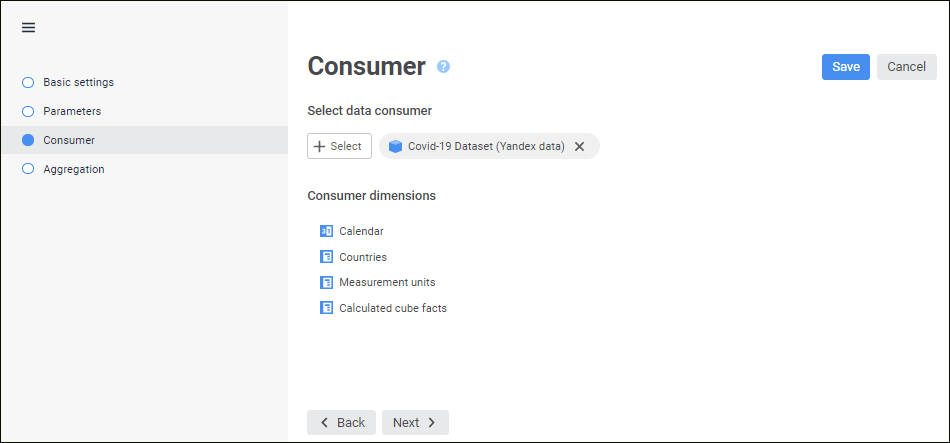
A consumer determines an object, in which data will be aggregated and loaded after a block is calculated. The following repository objects can be used as a data consumer:
A data consumer can be selected and set up on the Consumer page in the aggregation block editing wizard:

To select and set up a data consumer:
In the drop-down list select the object that will be used as a data consumer.
To quickly select an object, enter object's name/identifier/key in the search box depending on display settings. Search is executed automatically while the searched text is entered into the search string. The list will display the objects, which names/identifiers/keys contain the entered text.
To set up displaying of repository objects in the list, click the  Display Object button and select display option in the drop-down menu:
Display Object button and select display option in the drop-down menu:
Name. Objects are displayed with their names. Default option.
Identifier. Objects are displayed with their identifiers.
Key. Objects are displayed with their keys.
Several options can be selected. Identifier and key will be specified in brackets.
Set up filtering by elements for the selected dimension using the  Set Filter button located next to the data consumer dimension.
Set Filter button located next to the data consumer dimension.
After executing the operation the <dimension name> - filtering setup dialog box opens, in which determine data consumer dimension filtering settings.
As a result, the data consumer in the aggregation block is set up.
Filtering enables the user to calculate only parts of dimension elements.
To select the dimension elements, by which a block will be calculated, use the <dimension name> - filtering setup dialog box:
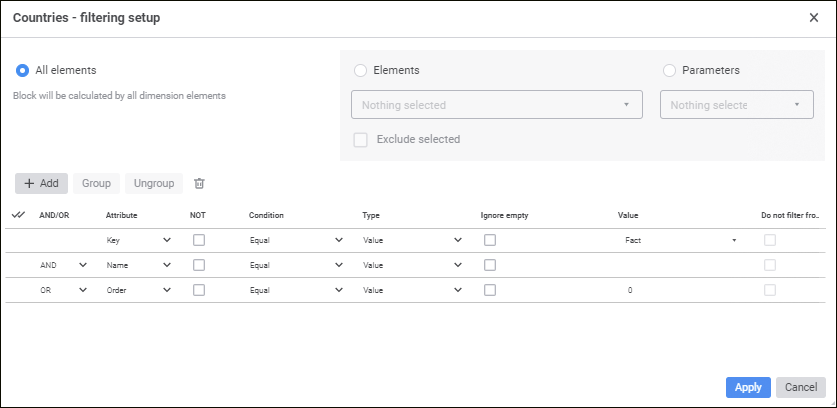
Setup order:
Select elements, by which a block should be calculated. Select one of the radio buttons:
All Elements. A block is calculated by all dimension elements.
Elements. A block is calculated by dimension elements selected in this list.
Parameters. A block is calculated by elements specified by a parameter. The option is available if a block contains parameters.
To work with dimension element selection use context menu items.
To calculate a block by all elements, except for the selected ones, select the Exclude Selected Elements checkbox.
Add advanced filtering conditions if required. Element attributes will correspond to the specified conditions during block calculation. Working with a group of condition parameters is identical to working with the Advanced Filter dialog box.
Click the Apply button.
After executing the operations the block is calculated only by elements corresponding to the configured filter.
NOTE. When calendar is used, a block is calculated at the intersection of calendar dimension selection specified in filtering settings, and algorithm calculation period specified on the parameters panel.
See also: