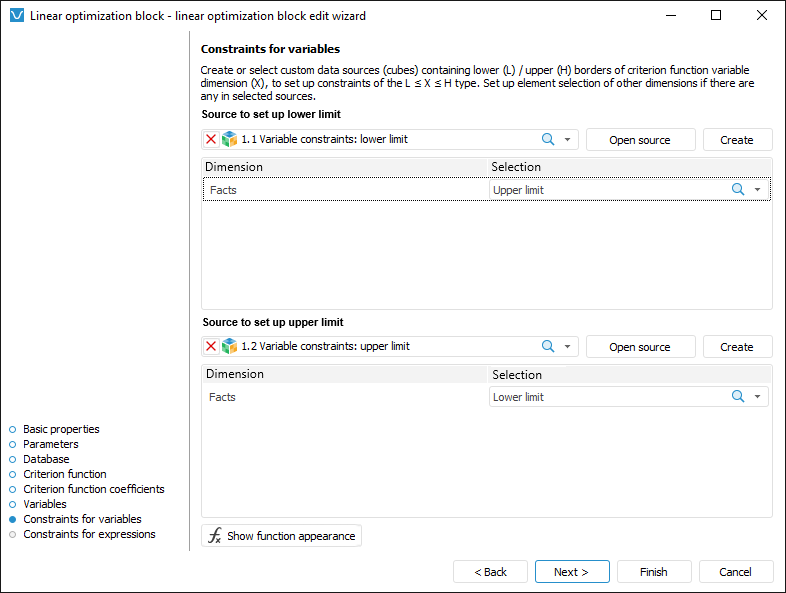
Constraints for variables enable the user to set simple conditions imposed on values of controlling variables. A condition is considered simple if it meet the following criteria:
It contains one controlling variable.
The 1 coefficient is set for the controlling variable.
For example, x1 ≥ 25 or 100 ≤ x2 ≤ 254, where x1 and x2 are controlling variables with the 1 coefficient. To set more complex conditions, use the Constraints for Expressions page in the linear optimization block editing wizard.
To set up simple constraints of controlling variables, use the Constraints for Variables page in the linear optimization block editing wizard.

Specify also the upper and lower constraint limits. Lower limit is a minimum allowed value of controlling variable, upper limit is a maximum allowed value of controlling variable. The following can be set for each controlling variable: only lower limit, only upper limit, both limits or no constraints.
For example, the constraint x1 ≥ 25 is set using only the upper limit. The constraint 100 ≤ x2 ≤ 254 requires to set both upper and lower limits.
Too enter simple constraints of controlling variables:
Select a data source to store values of upper and lower limits. This data source must contain all dimensions of controlling variables selected on criterion function setup. To create a data source with required structure, click the Create button.
Set selection by fixed dimensions of data source. If a custom data source is selected, the fixed dimensions contain all data source dimensions except for those used as dimensions of controlling variables. If the data source is used that is created in the linear optimization block editing wizard, only the Facts dimension is fixed with the only Value element selected by default.
Set values of limits. To do this:
Click the Open Source button. The data source is opened in the Analytical Queries (OLAP) tool. A data table is created as follows: rows contain all dimensions of controlling variables with the selection specified on criterion function setup; columns contain no dimensions; fixed dimensions and their selection are the same as those specified at step 2.
Enter values of limits for controlling variables to the table.
Go to the Data ribbon tab and click the  Save Changes button. It is requested to confirm the operation.
Save Changes button. It is requested to confirm the operation.
Close the Analytical Queries (OLAP) tool. It is prompted to save the report. Click the Cancel button.
If it is required to set values for limits of controlling variables for other values of fixed dimensions, change selection in them and repeat this step.
As a result, constraints of controlling variables are set.
To view the criterion function, click the Show Function External View button.
See also: