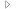 Example of registry file
Example of registry fileThe below example uses the OpenSSL version for Linux OS. The example shows steps for creating three certificates in the PEM format:
Root certificate is used to sign other certificates (ca.cer).
Server certificate is used by server to check user certificates (server.cer).
Client certificate is provided by a user to check at server (client.cer).
There are two types of configuration:
Desktop application > WEB Service driver > HTTPS > Security server (PP.SOM.SomSec) > DBMS.
Browser > HTTPS > web application at Apache2 server > HTTPS > BI server (PP.SOM.Som) > WEB Service driver > HTTP > Security server (PP.SOM.SomSec) > DBMS.
The configuration with BI server assumes connection with security server in internal network without using of HTTPS protocol.
NOTE. If it is required to use both connection configurations at a time, issue two server certificates (for BI server and security server) signed by one root certificate.
To install OpenSSL to Ubuntu/Debian/Astra Linux, execute the command:
sudo apt-get install openssl
To install OpenSSL to Red Hat Enterprise Linux, execute the command:
sudo yum install openssl
On creating a certificate a private key is generated that is used to decipher data encrypted by certificate's open part. For security purposes the key must be kept in secret and must not be passed to a third party.
First, create the openssl.cnf file containing additional information:
[ req ]
default_md = sha1
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
[ req_distinguished_name ]
countryName = Country
countryName_default = RU
countryName_min = 2
countryName_max = 2
localityName = Locality
localityName_default = Russia
organizationName = Organization
organizationName_default = Foresight
commonName = Common Name
commonName_max = 64
[ certauth ]
subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid:always,issuer:always
basicConstraints = CA:true
crlDistributionPoints = @crl
[ server ]
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = digitalSignature, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment
extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth
nsCertType = server
crlDistributionPoints = @crl
[ client ]
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = digitalSignature, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment
extendedKeyUsage = clientAuth
nsCertType = client
crlDistributionPoints = @crl
[ crl ]
URI=http://testca.local/ca.crl
If required, certificates in the PEM format can be converted to the DER format by the command:
openssl x509 -outform der -in MyCertificate.pem -out MyCertificate.crt openssl
To create a root certificate, execute the command:
openssl req -config ./openssl.cnf -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyform PEM -keyout ca.key -x509 -days 3650 -extensions certauth -outform PEM -out ca.cer
Additional data is requested on executing the command: PEM password and certificate owner data. On requesting the "Common name" specify name of the issuing certification authority, for example, Test CA.
Generate a key for server certificate:
openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048
Create a request for server certificate signing:
openssl req -config ./openssl.cnf -new -key server.key -out server.req
Issue a server certificate for 1 year:
openssl x509 -req -in server.req -CA ca.cer -CAkey ca.key -set_serial 100 -extfile openssl.cnf -extensions server -days 365 -outform PEM -out server.cer
On executing the command it is requested for a server domain name, for which server certificate is issued. Specify full computer name (the hostname command), if the computer is in the domain network and it will be addressed with specifying the domain, specify name including domain, for example, hostname.domain.ru/en.
The request for certificate creation contains a private key. After the certificate is issued, it is no longer required, for security purposes it must be deleted by the command:
rm server.req
Generate a key for a client certificate:
openssl genrsa -out client.key 2048
On executing the command it is requested to enter PEM password and answer follow-up questions. On requesting the "Common name" specify the user name, to whom the certificate is issued.
Create a request for issuing a client certificate:
openssl req -config ./openssl.cnf -new -key client.key -out client.req
Issue a client certificate:
openssl x509 -req -in client.req -CA ca.cer -CAkey ca.key -set_serial 101 -extfile openssl.cnf -extensions client -days 365 -outform PEM -out client.cer
Export the certificate and private key to the certificate in the PKCS#12 (PFX) format that contains the certificate and the encrypted key.
openssl pkcs12 -export -inkey client.key -in client.cer -out client.pfx
On export specify password for the private key that is required to import the certificate to storage.
Delete the client certificate in the PEM format, private key and request for certificate creation:
rm client.key client.cer client.req
As a result, the following is created:
Root certificate - ca.cer.
Server certificate - server.cer.
Client certificate with encrypted key - client.pfx.
Certificates must be placed as follows:
At server: root certificate and server certificate with key (ca.cer, server.cer and server.key).
At workstation: client certificate with encrypted key in the *.pfx format and root certificate without key.
The client certificate is installed into private user storage, the root certificate is imported into local computer's trusted root certification authorities storage.
Edit the PP.xml file located in the "config" folder of the web application to set up BI server connection avoiding proxy handler. Add the <AppConfig> section and the PPServiceUrl parameter:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<pp>
<service url="https://hostname.domain.ru/axis2/services/PP.SOM.Som" />
<AppConfig>
<Service PPServiceUrl="https://hostname.domain.ru/axis2/services/PP.SOM.Som"/>
</AppConfig>
</pp>
Determine the following settings for the repository in use:
Enable built-in authorization.
Create a p4audit service user.
Bind certificate fingerprint to the user.
Add connection settings for a security server:
Driver: WEB Service.
Connection point: http://hostname-ss.domain.ru/axis2/services/PP.SOM.SomSec.
Repository identifier: identifier of the repository created at security server.
NOTE. Connection settings are determined via the registry. Create necessary settings in the desktop application and copy them to BI server.
Add a repository with DBMS connection settings (via the registry). The security server workstation must have client programs of required DBMS installed.
Save data for database authorization by means of the PP.Util utility:
./PP.Util /save_creds <metabase_id> <login> <password>
In the settings.xml configuration file set the Strategy_check parameter.
After executing all the steps reload the web application, security server and BI server.
The further steps depend on the OS in use:
To check authorization by HTTP, open th URL: http://hostname.domain.com/fp9.2/app/login.html.
To check two-factor authorization by HTTPS, open the URL: https://hostname.domain.com/fp9.2/app/login.html.
When the page is opened, a client certificate is requested. Select the client certificate connected to the user account in use.
See also:
Setting Up Two-Factor Authentication | Example of Setting Up Two-Factor Authentication