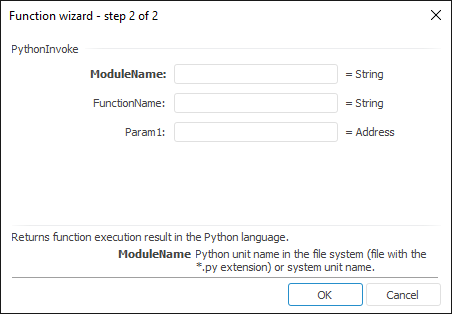
The function wizard for the PythonInvoke function looks as follows:

PythonInvoke(ModuleName, FunctionName, Param,…)
ModuleName. The Python module name in the file system or the system module name. When specifying the Python module in the file system, file with the * .py extension is used.
Search for the specified module:
In the Python installation folder next to the python3*.dll file or in the Scripts subfolder.
At the specified path, which is set with the help of the PythonPath string parameter in the registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Foresight\Foresight Analytics Platform\10.0\DevEnv\Python. For details see the Connecting External Modules to Foresight Analytics Platform section.
In the Foresight Analytics Platform installation folder.
FunctionName. Executed function name.
Param1, Param2, …, ParamN. Parameters sent to function.
NOTE. To define the parameter, specify either the number or the address of the cell where it is located.
It returns function execution result in the Python language.
NOTE. Before using the function, make sure that integration between Foresight Analytics Platform with Python is executed.
The function is outdated, use PythonInvokeModule.
The table contains examples of formulas using the PythonInvoke function:
| Formula | Result | Description |
| =PythonInvoke("math", "fabs", 4) | 4 | The module of the 4 number. |
| =PythonInvoke("math", "fabs", C3) | 4 | The module of the number from the C3 cell. The C3 cell contains the 4 number. |
| =PythonInvoke(C4, "fabs", C3) | 9 | The module of the number from the C3 cell. The C4 cell contains the "math" text value, the C3 cell - the -9 number. |
Parameters used in the formulas:
math. The system module of the Python language containing mathematical functions.
fabs. The Python system function, contained in the math module, that returns the absolute value of a number.
See also: