The tool supports interface of Foresight Analytics Platform 9 or earlier.
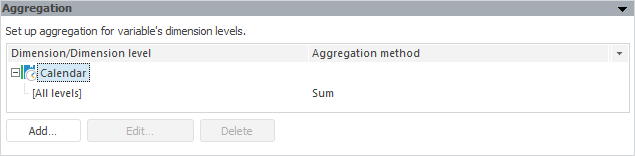
The panel is used to set up aggregation by levels of variable dimensions. Aggregation enables the user to calculate values at higher levels based on the values of lower levels.
The example of the Aggregation panel:

The Aggregation panel shows all dimensions that contain more than one level. Aggregation settings for dimension levels are shown as dimension child elements. Each level has an aggregation type displayed for it.
An aggregation type can be edited in the Set Up Basic Aggregation Mechanism or Set Up Chronological Aggregation Mechanism dialog boxes.
The basic aggregation mechanism can be used for all dimensions. Aggregation can be edited in the dialog box:
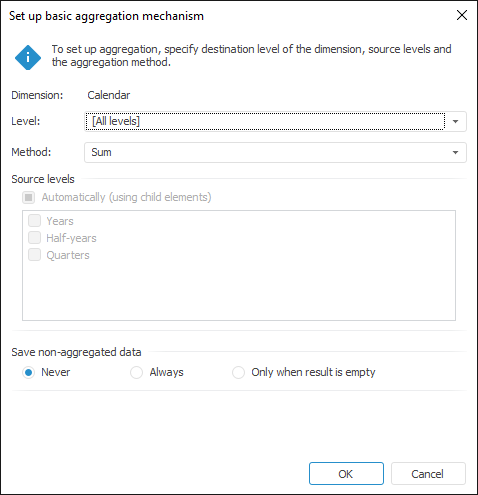
Set the parameters:
Level. Select a level in the drop-down list, for which aggregation should be set up. The list also contains the [All Levels] item, on selecting of which aggregation is set up equally for all dimension elements. Thus, if a new level is added into a dimension of a variable, the selected aggregation is automatically applied and calculated for this level.
When the aggregation is edited, the Level drop-down list is not available and shows the edited level.
Method. Specify the aggregation method. Available methods:
Sum. Source level elements are summed up.
Minimum. The minimum value is selected on the source level.
Maximum. The maximum value is selected on the source level.
Number of Non-Empty. The number of non-empty values is determined on the source level.
Number of Empty. The number of empty values is determined on the source level.
Number of All Children. The number of child elements is determined on the source level.
Average. The average of source level elements is determined taking into account empty values.
Actual Mean. The average of source level elements is determined ignoring empty values.
First Actual. The first actual value is taken on the source level.
Last Actual. The last actual value is taken on the source level.
Root-Mean-Square Deviation Based on a Sample. The root-mean-square deviation of a series based on a sample is determined.
Median. The median is determined for values on the source level.
Root-Mean-Square Deviation. The root-mean-square deviation of a series by the entire population is determined.
Number of Different Values. The number of different values is determined on the source level.
Source Levels. Select checkboxes of dimension levels that should be included into the aggregation. Selecting the Automatically (Using Child Elements) checkbox enables the user to use all elements in aggregation located one level below. If the [All levels] item is selected in the Level drop-down list, the Automatically (Using Child Elements) checkbox is automatically selected, and the Source Levels group becomes unavailable.
Save Non-Aggregated Data. The group contains radio buttons that determine parameters for saving non-aggregated data:
Never. Aggregated data is always saved to the destination level. Therefore, non-aggregated data is overwritten.
Always. Aggregated data is written to the destination level if there is no data at the destination level. Therefore, non-aggregated data is saved.
Only When Result is Empty. Aggregated data is saved to the destination level only if the aggregation result is empty. Therefore, non-aggregated data is saved.
If a dimension already contains aggregation by various levels, and you have set up aggregation for all levels in this dialog box, confirmation is required to change aggregation type.
Aggregation mechanism can be selected for a calendar dimension of a variable. To select a mechanism, use the context menu of the calendar dimension.
The basic aggregation mechanism is used by default (see above how to set up this mechanism). The dialog box looks as follows when a chronological mechanism is selected:
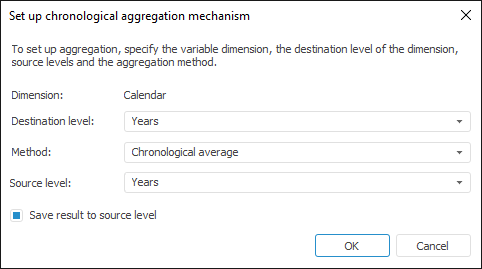
Determine the parameters: destination level, source level and aggregation method. The following methods are available:
Chronological Average. The value is calculated by the formula:
![]()
Where:
H. The chronological average of a series.
n. The number of points (days, months, and so on) of a series used for calculation.
m. The number of points (days, months, and so on) of a series that contain data.
P1. The series value for the start of the period, for which the chronological average is calculated.
Pn. The series value for the end of the period, for which the chronological average is calculated.
If the P1 and Pn points do not have any data, the value in the nearest point with the existing values to the 0.5 coefficient to P1 and Pn correspondingly.
The chronological average can be calculated within a month (the source level is days), within a quarter (the source level is days or months), within a year (the source level is days, months or quarters).
By default, aggregation results are loaded to the destination level and the source level. To load only destination level results, deselect the Save Result to Source Level checkbox.
Uniform Disaggregation. If this method is used, the value of a source level element is divided by the number of destination level elements. If this method is used, select the parent level as the source level and the child level as the destination level. For example, uniform disaggregation can be calculated for a day (the source level is months, quarters or years), for a month (the source level is years or quarters), for a quarter (the source level is years).
See also: