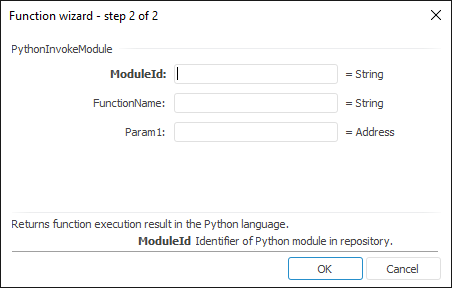
The function wizard for the PythonInvokeModule function looks as follows:

PythonInvokeModule(ModuleId,FunctionName,Param,…)
ModuleId. Unit with Python function in repository.
FunctionName. Function name
Param1, Param2, …, ParamN. Function parameter.
NOTE. To define the parameter, specify either the number or the address of the cell where it is located.
It returns function execution result in the Python language.
NOTE. Before using the functions written in the Python language, make sure that integration of Python and Foresight Analytics Platform is executed.
Function can contain several parameters. New formulas are added automatically in the formula wizard after the user outs the cursor into the field with parameter. If extra parameters are added, they should be left empty. If the function contains no parameters, leave the Param field empty.
Keep in mind the following when calling a Python function:
Function name is case-sensitive.
Parameters of the function and returned result must have one of the following data types: Null, Boolean, Integer, Double, Decimal (applied only to the result returned by the function), String
If input and output operations are used in the module, then use the mechanism of critical sections for them.
TIP. For details on writing functions in the Python language and on import of modules into the Python library, see Python documentation.
| Formula | Result | Description |
| =PythonInvokeModule("MOD_PYT", "calculate", 4, 40) | 4 | Calling the "calculate" function from Python unit in repository with the MOD_PYT identifier. Fixed values are sent as parameters values. |
| =PythonInvokeModule("MOD_PYT", "check", C3) | 4 | Calling the "check" function from Python unit in repository with the MOD_PYT identifier. The C3 cell value is sent as parameter value. |
See also: