 To display the tab
To display the tabThe method calculates data of the upper level based on the lower level data. It is used in problems, which need data aggregation. For example, data calculated for months is summed to get quarterly data.
NOTE. For data aggregation, the input variable calendar frequency must be less than the output variable frequency. If the input variable calendar frequency is greater or equal than the output variable frequency, the Collapse equation creation is not available.
To set up method parameters, use the Equation side panel tab.
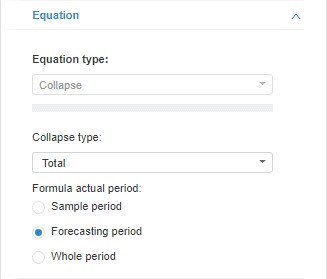
Method parameters:
Collapse Type. Specify aggregation method in use:
Total. Sum of frequency elements values. Default.
Average. Average of frequency elements.
Minimum. Minimum value of frequency elements.
Maximum. Maximum value of frequency elements.
First. First existing frequency elements value.
Last. Last existing frequency elements value.
Range. Difference between the maximum and the minimum frequency elements values.
Spread. Standard deviation of the frequency.
Formula Actual Period. Specify the period, on which data is aggregated:
Sample Period. Aggregation is calculated only based on sample period data.
Forecasting Period. Aggregation is calculated only based on forecasting period data.
Whole Period. Aggregation is calculated based on sample period and forecasting period data.
To set up period limits, use the Calculation Periods side panel tab.
See also:
Working with Equations | Time Series Analysis: Aggregation | IModelling.Collapse