Mind the following features on creating a model and working with it:
The object class Model- MetabaseObjectClass.KE_CLASS_MSMODEL.
The user must specify parent container because a model can be stored only within a container.
By default each created model contains annual frequency.
Use the IMsModel interface to work with a model using the Fore language. Using properties and methods of this interface, the user can set sample and forecasting periods for the model, as well as calculation method and set up other parameters.
NOTE. The examples given below require the objects listed in variable description section.
The user needs to set the output variable and its slice to work with parameters of model calculation method. The variable should be added to the collection of model input variables. After this the object implemented by the IMsFormula interface can be obtained for setting up model calculation options:
Sub UserProc;
Var
Model: IMsModel;
TransfModel: IMsFormulaTransform;
Varr: IMsVariable;
ModellingVar: IMsFormulaTransformVariable;
Tree: IMsFormulaTransformSlicesTree;
Slice: IMsFormulaTransformSlice;
Selector: IMsFormulaTransformSelector;
Formula: IMsFormula;
Begin
TransfModel := Model.Transform;
ModellingVar := TransfModel.Outputs.Add(Varr As IVariableStub);
Tree := ModellingVar.SlicesTree(ModellingVar);
Slice := Tree.CreateSlice(1);
Selector := TransfModel.CreateSelector;
Selector.Slice := Slice;
Formula := TransfModel.Transform(Selector);
End Sub UserProc;
Using properties and methods of the IMsFormula interface it is possible to change calendar frequency, determine and set up parameters for model calculation period.
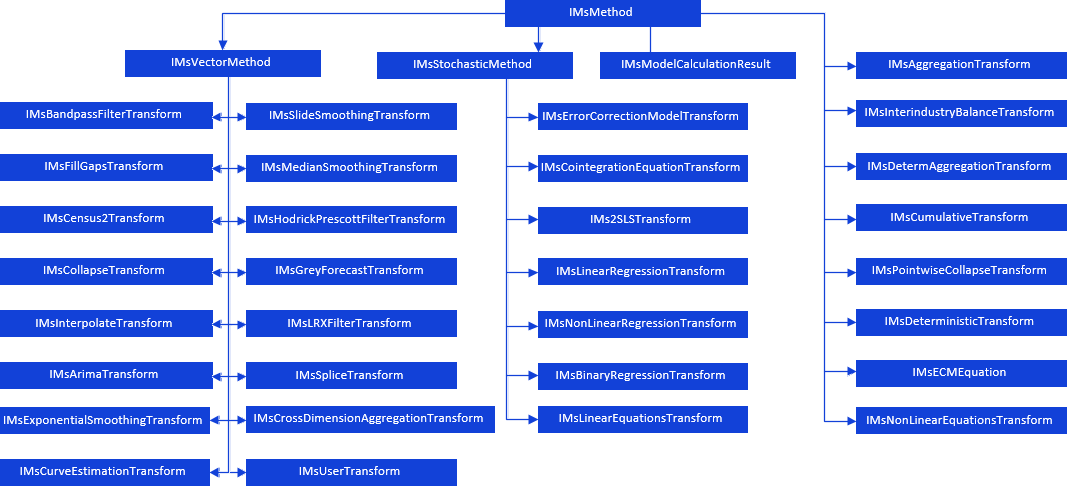
The model calculation method is implemented by the IMsMethod interface. This interface is a base one for all calculation methods:

Cast the IMsMethod interface to any child interface to set up a specific calculation method. For example, to calculate the Baxter-King filter, the IMsMethod interface should be cast to the IMsBandpassFilterTransform interface:
Sub UserProc;
Var
Formula: IMsFormula;
BPFilter: IMsBandpassFilterTransform;
Begin
Formula.Kind := MsFormulaKind.BandpassFilter;
BPFilter := Formula.Method As IMsBandpassFilterTransform;
End Sub UserProc;
Further programming of model parameters depends on model calculation method. For more details refer to description of appropriate interfaces.
After creating variables the user can create the Balance of Trade, billion USD model and set up its calculation options:
Output variable: Balance of Trade, billion USD.
Input variables: "Total Export, billion USD" and "Total Import, billion USD".
Model type: determinate equation.
Calculation formula: "Total Export, billion USD" and "Total Import, billion USD".
To run the unit to create and set up the Balance of Trade, billion USD model, add links to the Dimensions, Metabase, and Ms assemblies.
Sub UserProc;
Var
MB: IMetabase;
MsDescr, VarDescr: IMetabaseObjectDescriptor;
CrInf: IMetabaseObjectCreateInfo;
MObj: IMetabaseObject;
Model: IMsModel;
TransfModel: IMsFormulaTransform;
Varr: IMsVariable;
Var_Balance, Var_Exp, Var_Imp: IMsFormulaTransformVariable;
Tree: IMsFormulaTransformSlicesTree;
Slice: IMsFormulaTransformSlice;
Selector: IMsFormulaTransformSelector;
Formula: IMsFormula;
Determ: IMsDeterministicTransform;
Inputs: IMsFormulaTransformVariables;
Term_Exp, Term_Imp: IMsFormulaTerm;
Begin
MB := MetabaseClass.Active;
// Create a model
CrInf := Mb.CreateCreateInfo;
CrInf.ClassId := MetabaseObjectClass.KE_CLASS_MSMODEL;
CrInf.Id := "BALANCE_MODEL";
CrInf.Name := "Balance of Trade, billion USD";
MsDescr := Mb.ItemById("MODEL_SPACE");
CrInf.Parent := MsDescr;
MObj := Mb.CreateObject(CrInf).Edit;
Model := MObj As IMsModel;
// Get object to set up model parameters
TransfModel := Model.Transform;
// Set output variable
VarDescr := MB.ItemByIdNamespace("BALANCE", MsDescr.Key);
Varr := VarDescr.Bind As IMsVariable;
Var_Balance := TransfModel.Outputs.Add(Varr As IVariableStub);
Tree := Var_Balance.SlicesTree(Var_Balance);
Slice := Tree.CreateSlice(1);
Selector := TransfModel.CreateSelector;
Selector.Slice := Slice;
// Get object for setting up model calculation options
Formula := TransfModel.Transform(Selector);
Formula.Kind := MsFormulaKind.Deterministic;
Formula.Level := DimCalendarLevel.Year;
// Set up determinate equation calculation
Determ := Formula.Method As IMsDeterministicTransform;
Inputs := TransfModel.Inputs;
// Add the input variable Total Export, billion USD to the model
VarDescr := MB.ItemByIdNamespace("EXPORT", MsDescr.Key);
Varr := VarDescr.Bind As IMsVariable;
Var_Exp := Inputs.Add(Varr As IVariableStub);
Tree := Var_Exp.SlicesTree(Var_Exp);
Slice := Tree.CreateSlice(1);
Term_Exp := Determ.Operands.Add(Slice);
// Add the input variable Total Import, billion USD to the model
VarDescr := MB.ItemByIdNamespace("IMPORT", MsDescr.Key);
Varr := VarDescr.Bind As IMsVariable;
Var_Imp := Inputs.Add(Varr As IVariableStub);
Tree := Var_Imp.SlicesTree(Var_Imp);
Slice := Tree.CreateSlice(1);
Term_Imp := Determ.Operands.Add(Slice);
// Set model calculation formula
Determ.Expression.AsString := Term_Exp.TermToInnerText + " - " + Term_Imp.TermToInnerText;
MObj.Save;
Debug.WriteLine("The model is created and set up: '" + MObj.Name + "' with the identifier '" + MObj.Id + "'");
End Sub UserProc;
After executing the unit the Balance of Trade, billion USD model is created and set up with the BALANCE_MODEL identifier, and this information is displayed in the console window.
The next step is metamodel creation.
See also: