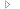 Fragment of the C:\Data.xlsx file for which the example is written
Fragment of the C:\Data.xlsx file for which the example is writtenFile: String;
The File property determines the entire name of the data provider file.
The name of the sheet, on which data is located, is determined by the IDtExcelProviderEx.Sheet property.
Executing the example requires the C:\Data.xlsx file.
Add a link to the Dt system assembly.
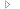 Fragment of the C:\Data.xlsx file for which the example is written
Fragment of the C:\Data.xlsx file for which the example is written
Sub UserProc;
Var
ExcelProviderEx: IDtExcelProviderEx;
Fields: IDtFieldDefinitions;
Field: IDtFieldDefinition;
FieldName, Val: String;
v: Array;
i: Integer;
s: double;
rez: boolean;
Begin
ExcelProviderEx := New DtExcelProviderEx.Create;
ExcelProviderEx.File := "C:\Data.xlsx";
ExcelProviderEx.Sheet := "Sheet1";
ExcelProviderEx.HasHeader := True;
ExcelProviderEx.HeaderRow := 0;
ExcelProviderEx.AutoFillFieldsMode := DtAutoFillFieldsMode.DataRow;
ExcelProviderEx.TypeGuessRows := 5;
ExcelProviderEx.Format := "XLSX";
ExcelProviderEx.DataRow := 1;
ExcelProviderEx.Open;
Fields := ExcelProviderEx.Fields;
Debug.WriteLine("Number of fields: " + Fields.Count.ToString);
FieldName := "Field names: ";
// Create a row with field names
For Each Field In Fields Do
FieldName := FieldName + Field.Name + "; "
End For;
Debug.WriteLine(FieldName);
Debug.WriteLine("Data:");
While Not ExcelProviderEx.Eof Do
Val := "";
ExcelProviderEx.Fetch(v);
// Create a row with data
For i := 0 To v.Length - 1 Do
rez := CultureInfo.Current.TryParseDouble(v[i], s);
If Not rez Then
val := val + v[i] + "; ";
Else
val := val + s.ToString + "; ";
End If;
End For;
Debug.WriteLine(val);
End While;
ExcelProviderEx.Close;
End Sub UserProc;
After executing the example the console window displays the data read from the specified file.
See also: