Policies: IABACPolicySets;
The Policies property is used to address the policies sets collection.
This property is relevant when attribute-based access control structure is determined.
To execute the example, make sure that there is the USERS group and an object with the 52 key.
Add links to the ABAC, Metabase, and Dal system assemblies.
Sub UserProc;
Var
PolicyObject: IABACRootPolicyObject;
PolicySet: IABACPolicySet;
Policy: IABACPolicy;
Rules: IABACRules;
Rule: IABACRule;
MB: IMetabase;
MS: IMetabaseSecurity;
Lic: Object;
Begin
MB:= MetabaseClass.Active;
// Get license to be able to work with security manager
Lic := MB.RequestLicense(UiLicenseFeatureType.Adm);
MS:= MB.Security;
// Activate the use of attribute-based access control
MS.Policy.AttributeBasedAccessControl := True;
PolicyObject := MS.Policy.ABACRules;
// Set attribute-based access control algorithm - Allow overriding
PolicyObject.CombineAlgorithm := ABACCombineAlgorithm.PermitOverride;
// Clear attribute-based access control structure
PolicyObject.Policies.Clear;
// Add a policies set
PolicySet := PolicyObject.Policies.Add;
PolicySet.Name(MB.CurrentLocale) := "Test policies set";
PolicySet.CombineAlgorithm := ABACCombineAlgorithm.PermitOverride;
// Add a policy
Policy := PolicySet.Policies.Add;
Policy.Active := True;
Policy.Name(LocaleCodeID.Russian) := "Test policy";
Policy.Id := "POLICY";
Policy.Description(LocaleCodeID.Russian) := "Policy contains rule for access to read object";
Policy.CombineAlgorithm := ABACCombineAlgorithm.PermitOverride;
Policy.Target.AttributeId := "SUBJECT.NAME";
Policy.Target.Operation := ABACTargetOperation.Equal;
Policy.Target.AttributeValue := "USERS";
// Add a rule
Rules := Policy.Rules;
Rule := Rules.Add;
Rule.Active := True;
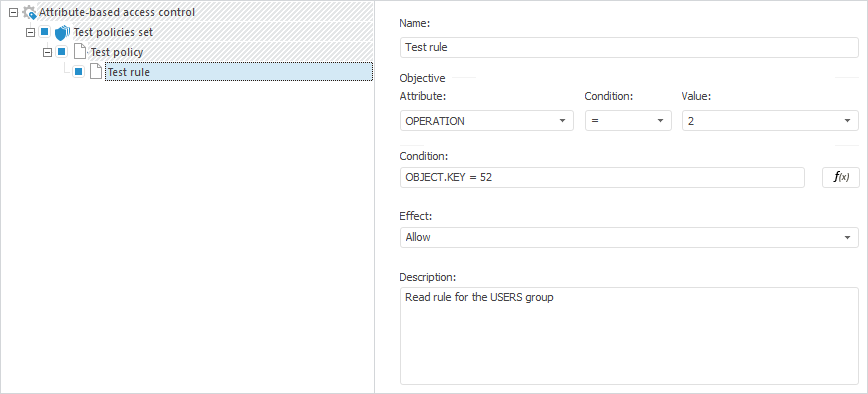
Rule.Name(LocaleCodeID.Russian) := "Test rule";
Rule.Id := "RULE";
Rule.Description(LocaleCodeID.Russian) := "Read rule for the USERS group";
Rule.Target.AttributeId := "OPERATION";
Rule.Target.Operation := ABACTargetOperation.Equal;
Rule.Target.AttributeValue := 2;
Rule.Condition.AsString := "OBJECT.KEY = 52";
Rule.Effect := ABACRuleEffect.Permit;
Debug.WriteLine("Rule key: " + Rule.Key.ToString);
// Apply changes in security manager
MS.Apply;
// Check in license
Lic := Null;
End Sub UserProc;
After executing the example the security manager activates the use of attribute-based access control, the specified attribute-based access control structure with specific rules is added, and the rules for access to read object in the USERS group are added:

The console displays the key of the new rule:
Rule key: 36
See also: