In the web application click the
 Create button in the main menu and select the object type on the New Object side panel.
Create button in the main menu and select the object type on the New Object side panel.
A dictionary is a linear or hierarchical list of elements containing brief and precise information on the same topic. Usually, dictionary data is arranged in accordance with a certain order (alphabetical, systematic, chronological, and so on) which makes it easy to quickly find required information.
In the multidimensional model of data, dictionary elements act as indexes, which are used to create a coordinate vector of indicators stored in cube cells. Dictionary elements have a set of attributes such as element name, unique code, and element order in the hierarchy. When elements in the dictionary are combined, the hierarchy – the most important property of a dictionary – emerges. As a rule, hierarchy is displayed as a tree, which nodes contain dictionary elements linked with attributes of ownership.
To create a dictionary in the object navigator:
In the web application click the  Create button in the main menu and select the object type on the New Object side panel.
Create button in the main menu and select the object type on the New Object side panel.
In the desktop application execute one of the operations:
Click the New Object > Dictionary button in the Create group on the Home ribbon tab.
Select the Create > Dictionary item in the object navigator's context menu.
Select a type of dictionary to be created on the Dictionary Type page in the dictionary wizard.
Dictionary wizard pages depend on dictionary type. After creating a dictionary, one can work with it.
Table dictionary. A dictionary is used for structured presentation of elements without the ability to add or edit them. To create a dictionary, one requires a table data set, MDM dictionary, or composite MDM dictionary. Each data source record is a dictionary element that must contain definitions of all dictionary attributes. The user can use various filters to limit the amount of data, which is loaded to the dictionary. A table dictionary can manage contents by means of parameters, that is, it is a dynamic dictionary. It can be created in any place of the repository:
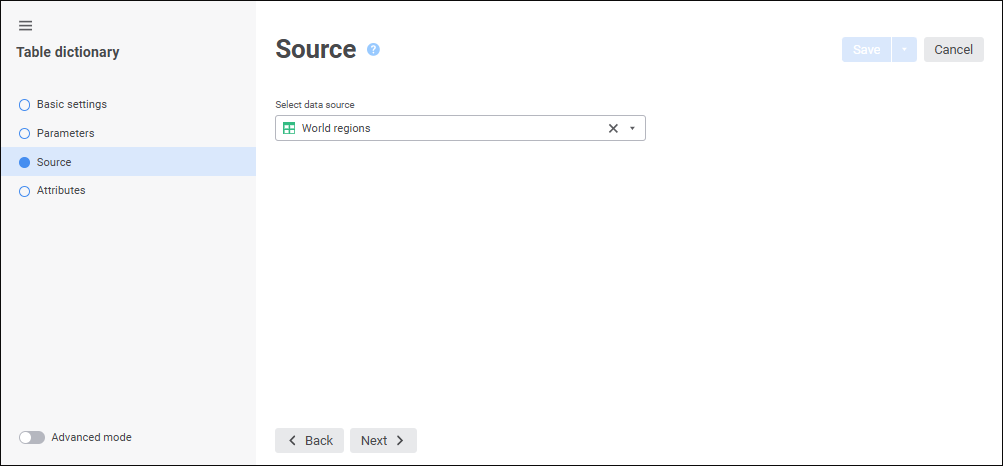
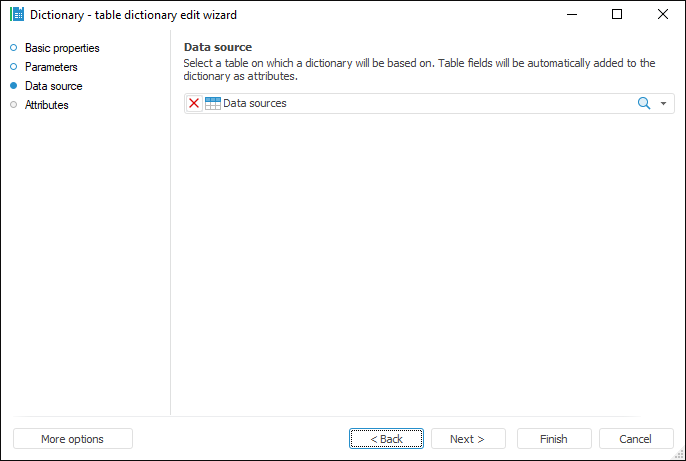
Calendar dictionary. It contains hierarchical view of time scale with defined drillthrough.
A calendar dictionary supports the following drillthrough levels: years, nine months, half-years, quarters, months, weeks, and days. Its contents is generated automatically depending on the specified parameters.
A calendar dictionary enables to dynamically define beginning and end of the time scale, that is, this is a dynamic dictionary.
Building this type of dictionary does not require creating tables and linking table elements. The user only needs to select calendar levels, whereas elements and their interaction are generated by the system:
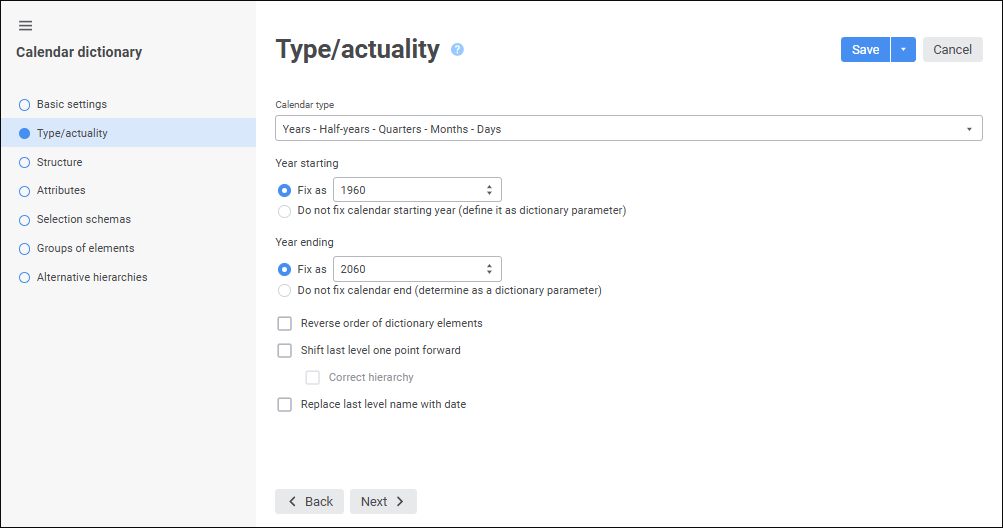
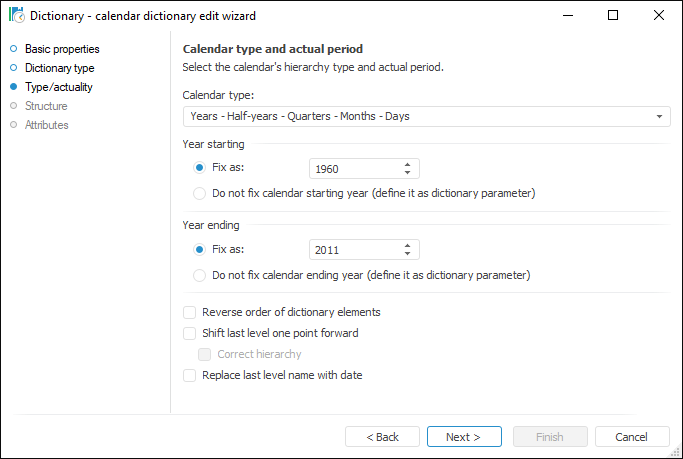
NOTE. A calendar dictionary does not support drillthrough by the time level, only date is taken into account.
Sub <Name>(UserDim: IUserDimension; Builder: IDimBuilder; Params: IMetabaseObjectParamValues);
Begin
//Code to create element tree for a calculated dictionary
End Sub <Name>;
A procedure and parameters can have any names satisfying the Fore language specification.
A unit is executed each time a dictionary is used. However, due to object caching in the platform this operation is automatically executed only if the unit is not available in cache, or when executing the Update operation. Generally, a calculated dictionary does not require a table to store its elements. Unit definition may include any repository objects, including data tables.
A calculated dictionary can be dynamically changed via parameters, that is, this is a dynamic dictionary:
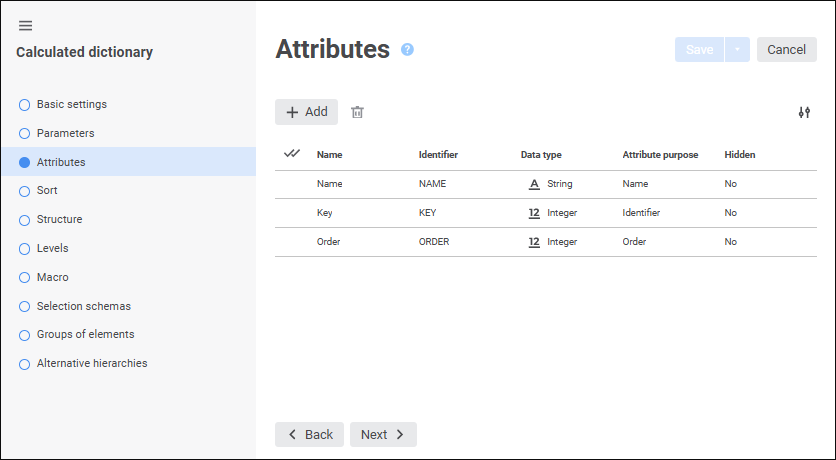
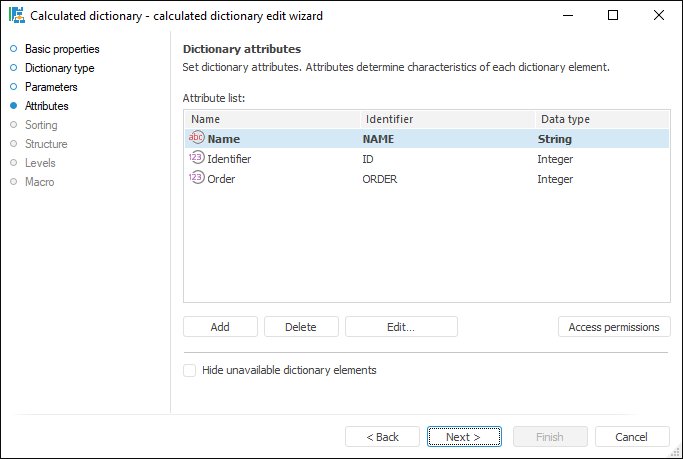
MDM dictionary. The dictionary is used to create a structured data presentation with the ability of its transformation. Creating a dictionary does not require a data source. Data can be entered manually or loaded from the data source to the dictionary by means of the built-in ETL tools. Dictionary elements may change in time, that is, may have several versions. An MDM dictionary can be created in any place of repository. An MDM dictionary uses a single table to store data. A table is created automatically on creating a dictionary and is the dictionary child object. Table fields correspond to dictionary attributes:
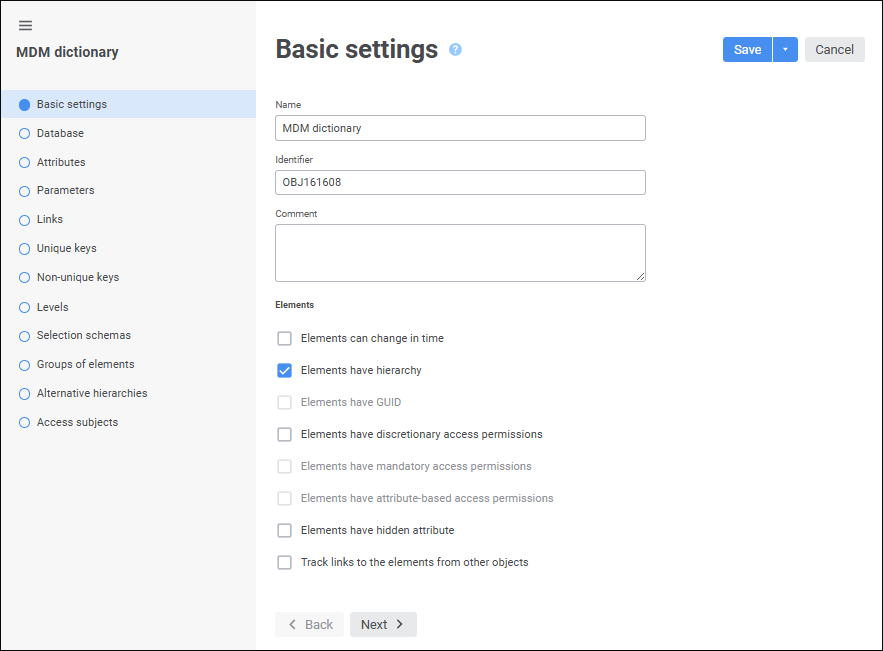
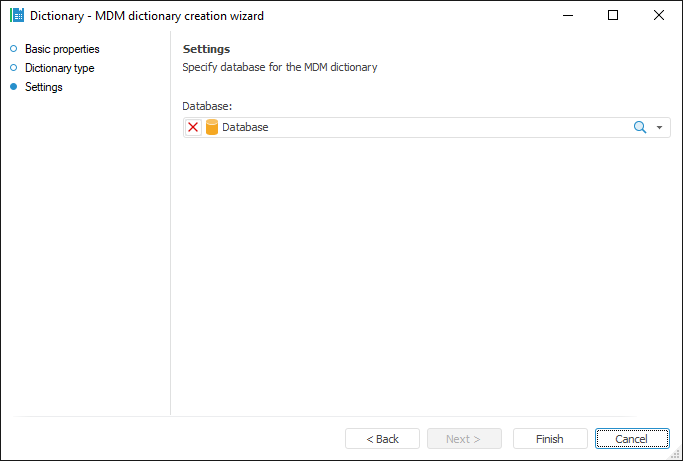
Composite MDM dictionary. An MDM dictionary which includes both its own elements and elements of other MDM dictionaries:
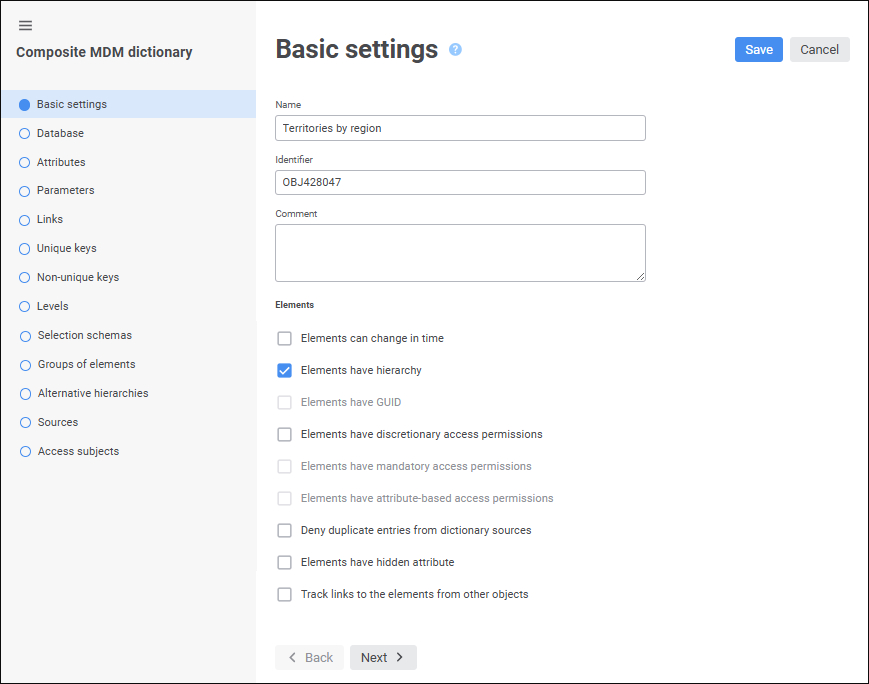
Depending on the dictionary structure, there are the following types of dictionaries:
Recursive dictionary. A dictionary with the number of levels that cannot be fixed at dictionary creation, as the number of levels depends on the data on which the dictionary is based.
Non-recursive dictionary. A dictionary with the number of levels fixed at its creation and independent on the data based on which the dictionary is created.
The dictionary can be:
Hierarchical. Dictionary elements are arranged at different levels of hierarchy and are linked by "parent-child" relations.
Non-hierarchical. Dictionary elements are arranged at one level of hierarchy and are not linked by "parent-child" relations.
See also: