Criterion function is the function, for which controlling variables must be selected so that the criterion function takes the minimum or maximum value.
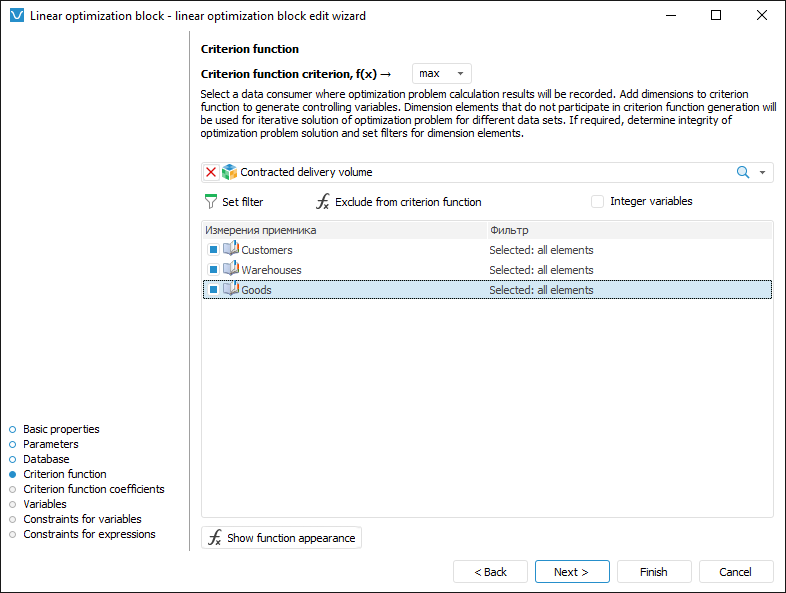
The purpose of criterion function, controlling variables and the data consumer, to which optimization results are loaded, are selected on the Criterion Function page in the linear optimization block editing wizard:

To create a criterion function:
Select criterion function optimization purpose in the Criterion Function Criterion, f(x) box:
min. Used by default. Values of controlling variables are selected so that the criterion function takes the minimum value.
max. Controlling variable values are selected so that the criterion function takes the maximum value.
Select the data consumer, to which block calculation results are loaded. It is assumed that all controlling variables in linear optimization block are based on data consumer dimensions. Therefore, the selected data consumer must contain the dimensions that enables the user to create a full set of controlling variables. If a dimension is used as a controlling variable, it is named a controlling variable dimension.
To select a data source, use the drop-down list located below the box for selecting criterion function optimization purpose.
Select controlling variable dimensions. To select a dimension, select its checkbox or select it in the list and click the Add to Criterion Function button. All the other dimensions are used for iterative solution of optimization problem.
To transform the controlling variable dimension into a normal dimension, deselect the checkbox or select the dimension in the list and click the Exclude from Criterion Function button.
To execute calculations only by elements, set up filtering by elements. To do this, select the dimension in the list and:
Click the  Set Filter button.
Set Filter button.
Double-click the dimension with the main mouse button.
The Set Up Filtering dialog box opens, in which determine data consumer dimension filtering settings.
IF all controlling variables are integer, select the Integer Variables checkbox. As a result, an linear optimization integer problem is solved. This problem is applied if controlling variables are atomic. For example, integer controlling variable is the number of cars in a transportation company. A car cannot be divided into two halves that is why it is atomic.
As a result, a criterion function is set up.
To view the criterion function, click the Show Function External View button.
Filtering enables the user to calculate only dimension elements.
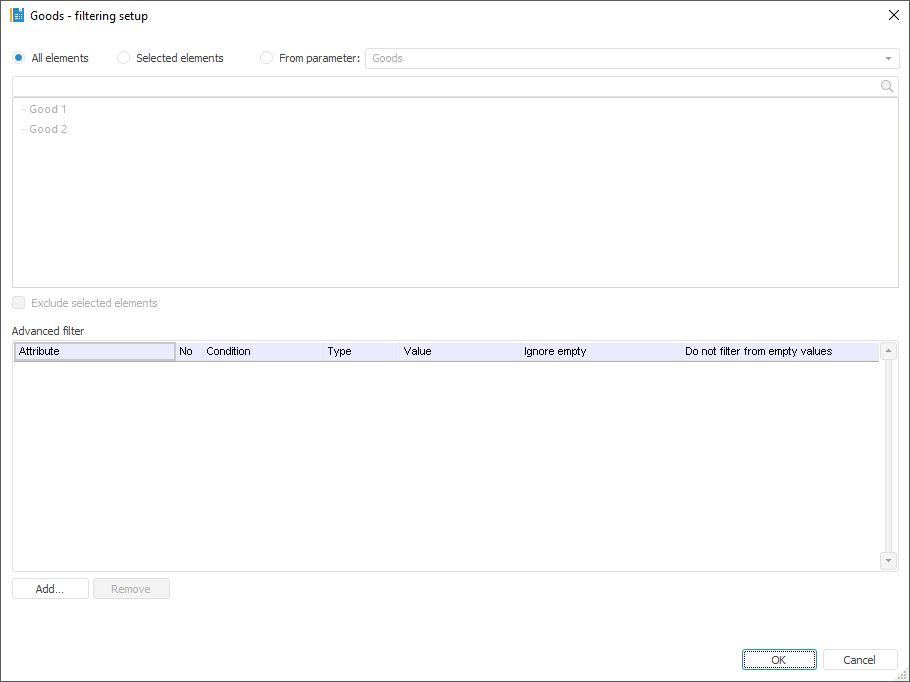
To select dimension elements, by which a block should be calculated, use the Set Up Filtering dialog box:
Setup order:
Select elements, by which a block should be calculated. Select one of the radio buttons:
All Elements. A block is calculated by all dimension elements.
Selected Elements. A block is calculated by dimension elements selected in this list.
From Parameter. A block is calculated by elements specified by a parameter. The option is available if a block contains parameters.
If it is required that a block is calculated by all the elements except for the selected ones, select the Exclude Selected Elements checkbox.
To set the conditions, with which element attributes must satisfy on block calculation, use the Advanced Filter group of parameters. Working with this group of parameters is similar to working with the Advanced Filter dialog box.
After executing the operations the block is calculated only by the elements corresponding to the filter.
See also: