Working with Java
Java is a cross-platform programming language. The Fore.NET language was developed for working with .NET Framework that is why this limits the use of platform resources when developing in Java. A special set of external libraries has been developed to provide work with Java in Foresight Analytics Platform. These libraries allow for working with Foresight Analytics Platform core. Java does not support work with forms (Fore/Fore.NET), components or dialog boxes available in Foresight Analytics Platform. To create user interface, use Java resources.
Connecting Assemblies
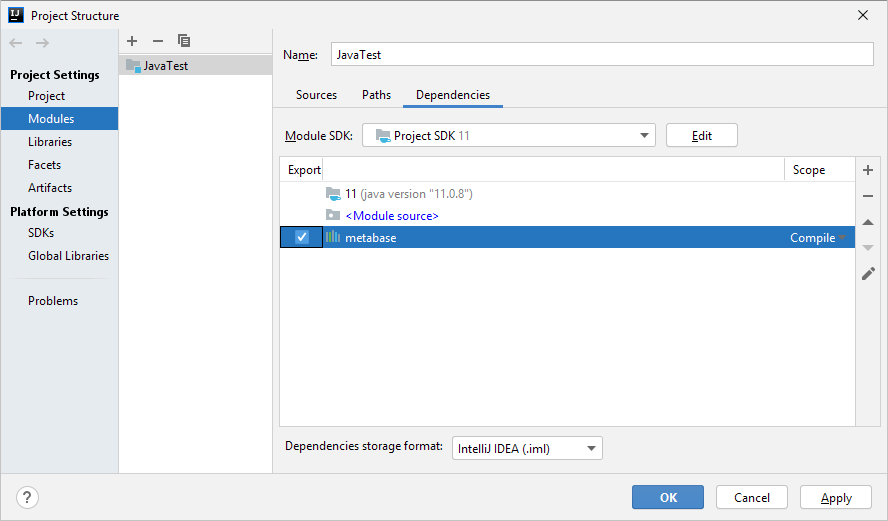
To connect an external assembly, enter the structure of the Java project to be developed, go to the Modules tab, click the  button and select the Library > Java item. In the dialog box that opens go to the folder with installed Foresight Analytics Platform and select the JAR file with the external assembly that corresponds with the required Fore assembly. Confirm the selection in the assembly configuration dialog box. In the project structure dialog box select the checkboxes next to the added assembly and click the Apply button. After this the resources of the added external assembly can be used in the Java code.
button and select the Library > Java item. In the dialog box that opens go to the folder with installed Foresight Analytics Platform and select the JAR file with the external assembly that corresponds with the required Fore assembly. Confirm the selection in the assembly configuration dialog box. In the project structure dialog box select the checkboxes next to the added assembly and click the Apply button. After this the resources of the added external assembly can be used in the Java code.
In the code enter the string with type import from the external assembly in one of the following formats:
import foresight.<assembly name>.*; //Import specified assembly contents
import foresight.<assembly name>.<type name>.*; //Import specified class/interface contents
Converting Code
When external assemblies are created, system classes, interfaces, enumerations and other types are specially converted to be used in Java. Therefore, take into account the following changes when creating a Java code using Foresight Analytics Platform resources:
All methods have two call options:
<method name>(<parameters>, Object [] objects). In this option, objects is an array, the first element of which saves the method call result.
do<method name>([<parameters>]). In this option, the method call result is in the returned value. It is recommended to use this option.
Properties have corresponding methods in the following formats:
get<property name>([<parameters>]) and set<property name>([<parameters>]). Get - gets property value, Set - sets property value.
get_<property name>([<parameters>], Object [] objects) and put_<property name>(<value>). Get returns property value to the first array element, and Put sets value and returns error code if the operation failed.
The C letter is added to class names for example: the MetabaseManagerFactory class in Fore corresponds with the CMetabaseManagerFactory class in Java.
To create an object of the required class, use the <Class name>.Create() or <Class name>.Create<interface name>() structure without the new keyword.
The enumeration elements are called in a standard way: <Enumeration name>.<Enumeration element name>. If it is required to cast the enumeration element to integer type, use the swigValue() method.
To cast types, create an object of the required type via "new" and pass the object as a parameter, for example:
ICredentials creds;
...
IPasswordCredentials pswdCreds = new IPasswordCredentials(creds);
The example of connecting to repository in the Java code:
import foresight.metabase.*; //Import entire assembly contents
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IMetabaseManager mbMan = CMetabaseManagerFactory.Create().getActive();
IMetabaseDefinitions mbDefs = mbMan.getDefinitions();
mbDefs.ReadFromRegistry();
IMetabaseDefinition mbDef = mbDefs.doFindById("FPRepository");
ISecurityPackage pack = mbDef.getSecurityPack();
ICredentials creds = pack.doCreateCredentials(AuthenticationMode.amPassword);
IPasswordCredentials pswdCreds = new IPasswordCredentials(creds);
pswdCreds.put_UserName("user");
pswdCreds.put_Password("password");
IMetabase mb = mbDef.doOpenDefault(pswdCreds);
// Display repository name
System.out.println(mb.getName());
}
}
See also:
Using Foresight Analytics Platform Resources in Third-Party Applications
 button and select the Library > Java item. In the dialog box that opens go to the folder with installed Foresight Analytics Platform and select the JAR file with the external assembly that corresponds with the required Fore assembly. Confirm the selection in the assembly configuration dialog box. In the project structure dialog box select the checkboxes next to the added assembly and click the Apply button. After this the resources of the added external assembly can be used in the Java code.
button and select the Library > Java item. In the dialog box that opens go to the folder with installed Foresight Analytics Platform and select the JAR file with the external assembly that corresponds with the required Fore assembly. Confirm the selection in the assembly configuration dialog box. In the project structure dialog box select the checkboxes next to the added assembly and click the Apply button. After this the resources of the added external assembly can be used in the Java code.