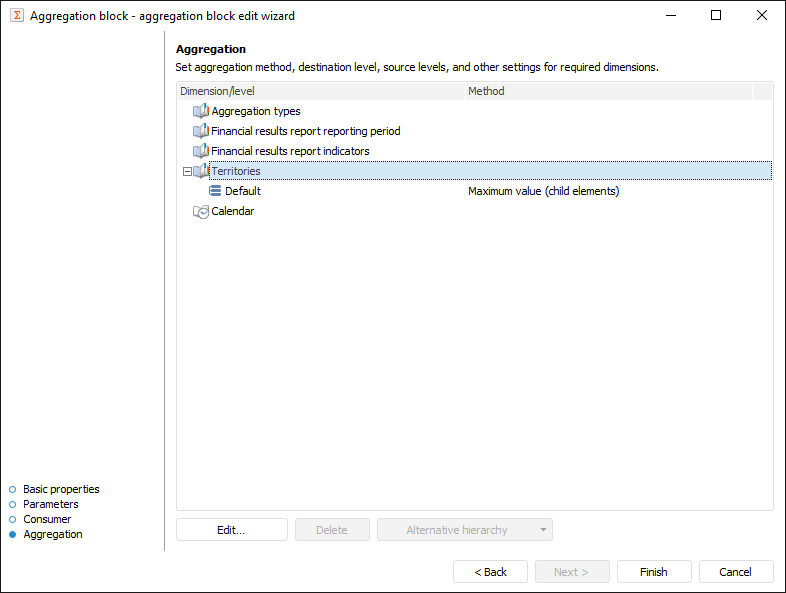
Aggregation setup determines, data by dimensions will be aggregated and by which method.
Aggregation can be set up on the Aggregation page in the aggregation block editing wizard:

To set up dimension aggregation:
Select the dimension to be aggregated.
Click the Edit button or double-click the dimension with the main mouse button.
The Set Up Aggregation dialog box opens, in which set dimension aggregation parameters.
If a dimension does not have alternative hierarchies, they can be used instead of standard dimension hierarchy. To select alternative hierarchy, use the drop-down menu of the Alternative Hierarchy button or the dimension's context menu. In the menu select the alternative hierarchy or the parameter that will be used to set alternative hierarchy.
If alternative hierarchy is selected for the dimension, the  icon is displayed for it. To reset alternative hierarchy and return to standard dimension hierarchy, select the Reset item in the drop-down menu of the Alternative Hierarchy button or in the dimension's context menu.
icon is displayed for it. To reset alternative hierarchy and return to standard dimension hierarchy, select the Reset item in the drop-down menu of the Alternative Hierarchy button or in the dimension's context menu.
As a result, dimension aggregation is set up. If required, similarly set up aggregation for the next dimension.
To delete the selected aggregation settings, click the Delete button.
To set up dimension aggregation parameters, use the Set Up Aggregation dialog box:
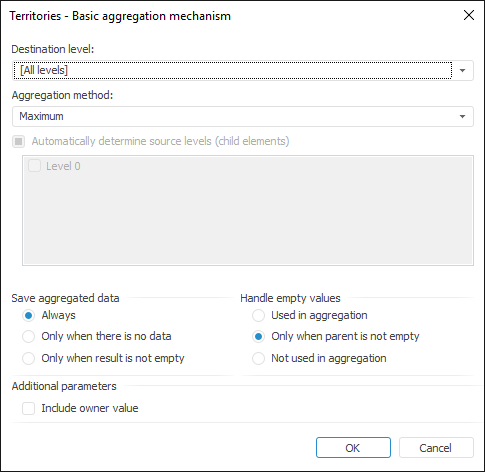
Setup order:
Select a destination level in the dimension, for which aggregation is set up. Use the Destination Level drop-down list. If the [All Levels] element is selected as a level, aggregation will be set up for all levels including those that can appear later.
Determine aggregation method in the Aggregation Method drop-down list. For details about available aggregation methods, see the Aggregation Methods section.
Determine source levels for aggregation.
To automatically determine source levels, select the Automatically Determine Source Levels (Child Elements) checkbox.
To manually determine source levels, make sure that the Automatically Determine Source Levels (Child Elements) checkbox is deselected and select checkboxes of all required levels.
If aggregation is set up for all levels, the source levels are always determined automatically.
Determine method of saving aggregated data at the destination level. Use the Save Aggregated Data group of radio buttons:
Always. Aggregated data is always written to the destination level.
Only When There Is No Data. Aggregated data is saved to the destination level if the destination level does not contain data.
Only when Aggregation Result is Not Empty. Aggregated data is saved to the destination level only if the aggregation result is not empty.
Determine empty values handling method. Use the Handle Empty Values group of radio buttons:
Used in Aggregation. Empty values will be used in aggregation.
Only When Parent is Not Empty. Empty values will be used in aggregation if parent element is not empty. If the result of aggregation by child elements is equal to empty value and the parent element already has value, it is replaced with empty value.
Not Used in Aggregation. Empty values will not be used in aggregation.
Determine whether the destination level value should be taken into account on aggregation calculation. By default, aggregation is calculated taking into account destination level. If the value is required to be excluded from aggregation, deselect the Include Owner Value checkbox.
As a result, aggregation for the selected dimension is set up.
If there are breaks in the selection, data is aggregated with jump to the level. A selection break occurs when child elements are selected, but their parent elements are no selected. In this case data of child elements of the non-selected parent element is used to calculate the next parent element.
For example, there is the hierarchy, in which there are breaks in elements selection:
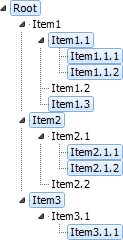
Data is aggregated with jump to the level as follows:
| Step | The Include Owner Value checkbox is selected. | The Include Owner Value checkbox is deselected. |
| Lower level value is calculated | ||
| Item 1.1 = Item 1.1 + item 1.1.1 + item 1.1.2 | Item 1.1 = item 1.1.1 + item 1.1.2 | |
| Upper level value is calculated | ||
| Item 2 = Item 2+ item 2.1.1 + 2.1.2 | Item 2 = item 2.1.1 + 2.1.2 | |
| Item 3 = Item 3 + item 3.1.1 | Item 3 = item 3.1.1 | |
| Root element value is calculated | ||
| Root = Root + item 1.1 + item 1.3 + item 2 + item 3 | Root = item 1.1 + item 1.3 + item 2 + item 3 | |
The following methods are available to aggregate dimension in matrix aggregation model:
None. No aggregation.
Sum. Source level elements are summed up.
Minimum. The minimum value is selected at the source level.
Maximum. The maximum value is selected at the source level.
Number of Non-Empty. The number of non-empty values is determined at the source level.
Number of Empty. The number of empty values is determined at the source level.
Number of All Children. The number of child elements is determined at the source level.
Arithmetic Mean. The arithmetic mean of the level elements, considering empty values, is determined.
Actual Mean. The actual mean value of the level elements, not considering empty values, is determined.
First Actual. The first actual value is taken at the source level.
Last Actual. The last actual value is taken at the source level.
Root-Mean-Square Deviation by Sampling. Root-mean-square deviation is defined for row based on sample.
Median. Determines a median for source level values.
Root-Mean-Square Deviation. Determines a root-mean-square series deviation based on the entire population.
Number of Different Values. The number of unique values is determined at the source level.
See also: