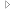 Executing Fore.NET method results in error of missing registered COM class
Executing Fore.NET method results in error of missing registered COM classForeExecResult ForeExec(ForeId tFore, ForeExecArg tArg)
tFore. Moniker of the development environment object that contains implementation of the executed method.
tArg. Operation execution parameters.
The ForeExec operation executes methods implemented in Fore or Fore.NET units and assemblies.
To execute the operation, in the tFore field specify moniker of the unit, assembly or .NET assembly that contains implementation of the executed method. The moniker can be obtained on executing the GetObjects operation. In the tArg.methodName field determine name of the method to be executed, and in the tArg.args field determine values of the method input parameters. If the method is within the Fore unit or assembly, its implementation must be contained in the global namespace. As the value of the tArg.methodName field determine name of the method to be executed. If the method is within the Fore.NET assembly, its implementation must be contained in a class. The executed method must have the Public and Shared access modifiers. Method name in the "class"."method" format is determined as a value of the tArg.methodName field.
Method signature must contain simple types parameters and return a simple type value. If the method returns a value, this value is available in the operation execution result.
If the executed method contains parameters with the Object type, string views of any object's monikers must be sent as values of these parameters. On executing the operation by the moniker the appropriate repository object is obtained and sent to the executed method. To work with this object, cast it to the interface that describes its structure. For example, on passing repository connection moniker, the parameter in method will be of the IMetabase type, on passing express report moniker it will be of the IEaxAnalyzer type, and so on.
See below a list of various problems that may occur on using the ForeExec operation and solutions.
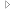 Executing Fore.NET method results in error of missing registered COM class
Executing Fore.NET method results in error of missing registered COM class
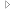 Executing Fore.NET method results in the "Catastrophic failure" error
Executing Fore.NET method results in the "Catastrophic failure" error
On developing the web application, from which various Fore or Fore.NET methods are supposed to be run, use the following recommendations:
Use ForeExec to execute the code, which makes simple calculations or operations that are not time and resource intensive.
If the code executes resource-intensive operations (report calculation, loading or transformation of large data sets, and so on), it is recommended to think about using a scheduled tasks container, that is, to create a unit or .NET assembly execution task, use operations for working with scheduled tasks container to control the task.
If a scheduled tasks container cannot be used, the code that executes resource-intensive operations must be transferred to .NET assembly in a separate stream.
When selecting BI server configuration, take into account possible resource-intensive operations that must have been executed in parallel by means of ForeExec. The number of processor cores (physical and logical) must be not less than the number of possible resource intensive operations running in one stream.
Due to possible use of the ForeExec operation for executing the code, to which the particular user must not have access, it is available to disable executing of the operation:
Create the Disallow parameter with the 1 value in the BI server settings file Settings.xml. Operation execution is enabled or disabled by BI server.
Create the foreExec parameter with the False value in the web server settings file PP.xml. Operation is enabled or disabled by web server. In this case to disable operation, the p_h parameter with the 1 value is automatically created in the request title.
NOTE. For details about location of parameters see description of the appropriate configuration files.
Create the p_h or p-h parameter with the 1 value in the title of the request that executes the ForeExec operation. The parameter is created by means of resources of the programming language that is used for development according to the application logic. For example, the code developed with JavaScript will be the following:
<html>
<body>
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
<!--...Previous application code...-->
<!--...-->
<!--Function for sending JSON request-->
function PostRequest(url, request) {
<!--...-->
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
<!--...-->
xhr.setRequestHeader('p-h', '1');
<!--...-->
xhr.send(JSON.stringify(request));
<!--...-->
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Various ways of using this operation are given in the following examples:
| Example name |
See also: