Attribute editing is used to convert real input data into categorical one in the following analysis types:
Clustering (for the K-modes method).
Pattern Substitution (for the Decision Tree and Logistic Regression, Decision Tree Ensembles).
NOTE. Attribute editing is available only in the desktop application.
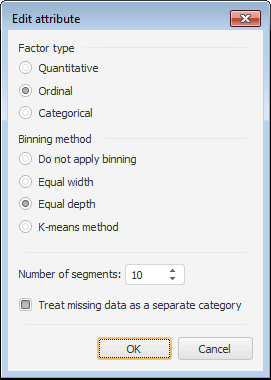
To determine settings of the selected attribute or a factor affecting the analyzed attribute, use the Edit Attribute dialog box:

Set the following options:
Factor Type. Determine type of the factor that affects the analyzed attribute.
Quantitative. A data set, which elements can be ordered, and the distance between them can be found. For example, car fuel consumption. The values can be ordered, which enables the user to conclude who has more and who has less.
Ordinal. A data set, which elements can be ordered, but the distance between them cannot be found. For example, internet shop order status: processing payment (0), order is sent (1), order is shipped (2), order is delivered (3), order is received (4), dispute is opened (5), dispute is closed (6). The order is clear, but the distance between elements in this array cannot be found.
Categorical. A data set, which elements cannot be ordered, and the distance between them cannot be found. For example, what is an usual food for people from the sampling: a sandwich, cereal, scrambled eggs, and so on. It is not possible to order the array elements, neither find the distance between them.
NOTE. The factor type can be selected only in the Decision Tree Ensembles method.
Binning Method. Determine the split method for the input data array:
Do not Apply Binning. The data array will not be split into groups.
Equal Width. The data array will be split into segments with equal width.
Equal Depth. The data array will be split into segments containing equal number of values.
K-Means Method. Data array will be split into segments by the K-Means method.
Number of Segments. Specify the number of segments to split the data array into.
Treat Missing Data as a Separate Category. Determine whether missing data is treated as a separate category. By default the checkbox is selected, and missing data is selected into a separate category.
NOTE. The Treat Missing Data as a Separate Category parameter is available only on factor setup.
See also: