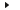 Example of the PP.xml file that contains settings for working with plugins
Example of the PP.xml file that contains settings for working with pluginsA plugin is a separately written block that can be connected to a dashboard.
On working with plugins in the desktop application, units written in the Fore language are used. To work in the web application, a plugin must be written on JavaScript.
Plugins are registered in general repository parameters and refer to the Fore unit for working in the desktop application and to the script for working in the web application.
To display a plugin in the web application:
Register a plugin that has a link to the script in the services.
Plugin is registered in the desktop application, a link to a *.js file is set on plugin registration in Fore by the .WebUrl property, for example:
plugin.WebUrl := "http://test/PP_App_v9.0/app/plugin.js";
Script of the plugin registered via the services must contain the code that registers its settings.
The ServicesPlugins property is set by two methods:
For the entire web application in the PP.xml file. Add the following code inside the <pp> tag:
<AppConfig>
<Modules>
<Dashboard>
<ReportBox ServicesPlugins="true"/>
</Dashboard>
</Modules>
</AppConfig>
After file editing restart the web server used by the web application.
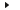 Example of the PP.xml file that contains settings for working with plugins
Example of the PP.xml file that contains settings for working with plugins
On creating an instance of the KapBox component, for example:
kapBox = new Kap.KapBox({
Metabase: metabase,
ParentNode: "DashboardBox",
Key: ppKey,
Mode: ppMode,
ServicesPlugins: true
});
A plugin can be connected by the user without registration in repository services.
Use the regPluginBlock method of the Kap namespace for the user registration of plugin, for example:
Kap.regPluginBlock({
Id: "SourceLabel", //id, by which plugin block is connected to its implementation
Name: "Source label", //readable name of block type
View: "PP.Ui.MyLabel", //visualizer class or visualizer class name
Master: "PP.Ui.MyMaster", //wizard class or wizard class name
Icon: "../build/img/app/MainIcon.png", //path to the icon (16*16) for plugin, optional parameter
SourceClass: 2561, //code of data source class, if it is not set, dashboard designer does not give a source for the plugin
Js: "pluginBlocks.js" // for dynamic loading of script with plugin implementation, optional parameter
});
On writing a plugin and new classes use code writing recommendations.
Prognoz Platform 9 assemblies contain several examples of plugins:
PP.RadiusAngleChartPlugin.js.
PP.RatingCartPlugin.js.
PP.TrellisPlugin.js.
A plugin connected via the services must call the Kap.regPluginBlock method for registering plugin settings in the web application, for example:
PP.Exp.Ui.EaxRadiusAngleChartView.init = function ()
{
if (window.Kap)
Kap.regPluginBlock({
Id: "RadiusAngleChart",
Name: "RadiusAngleChart",
View: "PP.Exp.Ui.EaxRadiusAngleChartView",
SourceClass: PP.App.ModuleType.Olap,
Js: "EaxRadiusAngleChart.js"
});
};
On registering plugin settings by the Kap.regPluginBlock method it is available to set additional plugin parameters in the Props property:
Props: { // for setting default values for some block plugin properties, optional parameter
"name": "default name",
"decor": {
"useBorder": "false"
},
"pluginProps": "{ <plugin properties>}"
}
The Refreshed and PropertyChanged events must be determined for a plugin visualizer.
If a plugin must work with a data source, create implementation of the setSource(source) method, the SourceClass property, set on plugin registration, is responsible for source type.
If a plugin must support stored properties, set implementation of the getProps(), setProps(value) methods.
If a plugin must have its own context menu, redetermine the method PP.Ui.Control.getContextMenu(sender).
If additional side panel tabs must be displayed for the plugin, that contain plugin settings, create implementation of the setDataView(view) method, where view is an instance of plugin visualizer. On plugin setup set the Master property that contains an instance of plugin visualizer.
See also:
Code Writing Recommendations | Registering Plugin in the Desktop Application